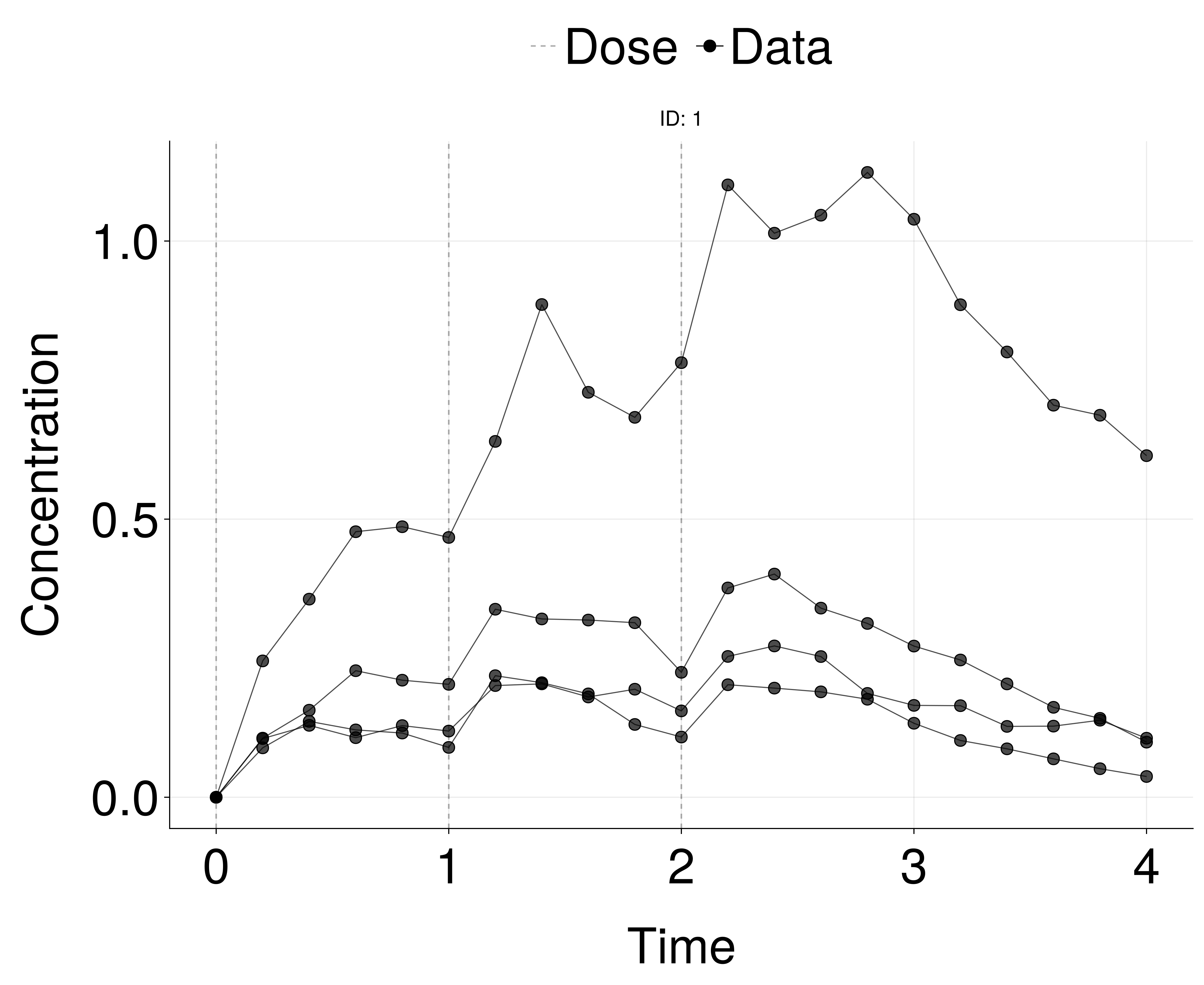
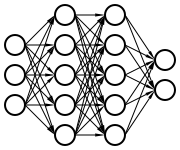
DeepNLME
Neural Networks, SciML, and Universal Differential Equations
2025-10-12
NLME Modeling
Traditional NLME
Typical values \[ tvKa, \; tvCL, \; tvVc, \; Ω, \; σ \]
Covariates \[ Age, \; Weight \]
Random effects \[ η \sim MvNormal(Ω) \]
Individual parameters \[\begin{align*} Ka_i &= tvKa \cdot e^{η_{i,1}} \\ CL_i &= tvCL \cdot e^{η_{i,2}} \\ Vc_i &= tvVc \cdot e^{η_{i,3}} \end{align*}\]
Dynamics \[ \begin{align*} \frac{dDepot(t)}{dt} =& - Ka \cdot Depot(t) \\ \frac{dCentral(t)}{dt} =& Ka \cdot Depot(t) - \frac{CL}{Vc} \cdot Central(t) \end{align*} \]
Error model \[ dv(t) \sim Normal\left(\frac{Central(t)}{Vc}, \frac{Central(t)}{Vc} \cdot σ\right) \]
What if components are unknown?
Typical values \[ tvKa, \; tvCL, \; tvVc, \; Ω, \; σ \]
Covariates \[ Age, \; Weight, \; \color{red}{???} \]
Random effects \[ η \sim MvNormal(Ω) \]
Individual parameters \[\begin{align*} Ka_i &= tvKa \cdot e^{η_{i,1}} \\ CL_i &= tvCL \cdot e^{η_{i,2}} \cdot \color{red}{???} \\ Vc_i &= tvVc \cdot e^{η_{i,3}} \end{align*}\]
Dynamics \[ \begin{align*} \frac{dDepot(t)}{dt} =& - Ka \cdot Depot(t) \\ \frac{dCentral(t)}{dt} =& Ka \cdot Depot(t) - \color{red}{???} \end{align*} \]
Error model \[ dv(t) \sim Normal\left(\frac{Central(t)}{Vc}, \frac{Central(t)}{Vc} \cdot σ\right) \]
Neural networks
Information processing mechanism
- Loosely based on neurons
- Mathematically just a function!
- Usable anywhere you’d use a function!
Neural networks in NLME dynamics
Typical values \[ tvKa, \; tvCL, \; tvVc, \; Ω, \; σ \]
Covariates \[ Age, \; Weight \]
Random effects \[ η \sim MvNormal(Ω) \]
Individual parameters \[\begin{align*} Ka_i &= tvKa \cdot e^{η_{i,1}} \\ CL_i &= tvCL \cdot e^{η_{i,2}} \\ Vc_i &= tvVc \cdot e^{η_{i,3}} \end{align*}\]
Dynamics ← This lecture focuses here \[ \begin{align*} \frac{dDepot(t)}{dt} =& - Ka \cdot Depot(t) \\ \frac{dCentral(t)}{dt} =& Ka \cdot Depot(t) - \color{red}{NN(...)} \end{align*} \]
Error model \[ DV(t) \sim Normal\left(\frac{Central(t)}{Vc}, \frac{Central(t)}{Vc} \cdot σ\right) \]
Scientific Machine Learning
Neural-embedded dynamical systems
2018 - “Neural Ordinary Differential Equations”, Chen et al.
2020 - “Universal Differential Equations for Scientific Machine Learning”, Rackauckas et al.
Neural ODE
\[ \frac{d\mathbf{X}}{dt} = NN(\mathbf{X}(t), t) \]
- ODE solver as scaffold for neural networks
- Similar to recurrent neural networks and ResNets
- Pure machine learning approach
Universal Differential Equations (UDE)
\[\begin{align*} \frac{dx}{dt} &= x \cdot y - NN(x)\\ \frac{dy}{dt} &= p - x \cdot y \end{align*}\]
- Insert universal approximators (NNs) to capture unknown terms
- Combine scientific knowledge with machine learning
- More data-efficient than pure ML approaches
Scientific Machine Learning (SciML)
- Abstract idea: mixing science and machine learning
- Umbrella term for hybrid approaches
- Includes UDEs, Physics-Informed NNs, etc.
- Goal: leverage domain knowledge to improve ML
Encoding Knowledge
Pure Neural ODE \[ \begin{aligned} \frac{dDepot}{dt} &= NN(Depot, Central, R)[1]\\ \frac{dCentral}{dt} &= NN(Depot, Central, R)[2]\\ \frac{dR}{dt} &= NN(Depot, Central, R)[3] \end{aligned} \]
- Number of states
Graph Neural ODE \[ \begin{aligned} \frac{dDepot}{dt} &= - NN_1(Depot)\\ \frac{dCentral}{dt} &= NN_1(Depot) - NN_2(Central)\\ \frac{dR}{dt} &= NN_3(Central, R) \end{aligned} \]
- Number of states
- Dependencies
- Conservation principles
UDE \[ \begin{aligned} \frac{dDepot}{dt} &= - K_a \cdot Depot\\ \frac{dCentral}{dt} &= K_a \cdot Depot - CL/V_c \cdot Central\\ \frac{dR}{dt} &= NN_3\left(\frac{Central}{V_c}, R\right) \end{aligned} \]
- Explicit knowledge of some terms
- Neural networks only where needed
Targeted Neural Enhancement (still a UDE) \[ \begin{aligned} \frac{dDepot}{dt} &= - K_a \cdot Depot\\ \frac{dCentral}{dt} &= K_a \cdot Depot - CL/V_c \cdot Central\\ \frac{dR}{dt} &= k_{in} \cdot \left(1 + NN\left(\frac{Central}{V_c}\right)\right) - k_{out} \cdot R \end{aligned} \]
- Most knowledge encoded!
- Neural network captures unknown drug effect
- Precise positioning and inputs
DeepNLME for Longitudinal Data
Extending for longitudinal data with DeepNLME
\[\begin{equation} η \sim \mathcal{N}\left(Ω\right) \end{equation}\] \[\begin{align*} Ka &= tvKa \cdot e^{η_{2}} \\ V_c &= tvV_c \cdot e^{η_{3}} \\ Kout &= tvKout \cdot e^{η_{4}} \end{align*}\]
\[\begin{align*} \frac{\mathrm{d} Depot(t)}{\mathrm{d}t} &= - Ka \cdot Depot(t) \\ \frac{\mathrm{d} Central(t)}{\mathrm{d}t} &= \frac{ - CL \cdot Central(t)}{V_c} + Ka \cdot Depot(t) \\ \frac{\mathrm{d} R(t)}{\mathrm{d}t} &= Kin \cdot \left( 1 + NN\left(\frac{Central}{V_c} \right) \right) - Kout \cdot R(t) \end{align*}\]
\[\begin{align*} yPK &\sim \mathrm{Normal}\left( \frac{Central}{V_c}, σ_{pk} \right) \\ yPD &\sim \mathrm{Normal}\left( R, σ_{pd} \right) \end{align*}\]
Individual-level neural networks
\[\begin{equation} η \sim \mathcal{N}\left(Ω\right) \end{equation}\] \[\begin{align*} Ka &= tvKa \cdot e^{η_{2}} \\ V_c &= tvV_c \cdot e^{η_{3}} \\ Kout &= tvKout \cdot e^{η_{4}} \end{align*}\]
\[\begin{align*} \frac{\mathrm{d} Depot(t)}{\mathrm{d}t} &= - Ka \cdot Depot(t) \\ \frac{\mathrm{d} Central(t)}{\mathrm{d}t} &= \frac{ - CL \cdot Central(t)}{V_c} + Ka \cdot Depot(t) \\ \frac{\mathrm{d} R(t)}{\mathrm{d}t} &= Kin \cdot \left( 1 + NN\left(\frac{Central}{V_c}, {\color{orange} η₁} \right) \right) - Kout \cdot R(t) \end{align*}\]
\[\begin{align*} yPK &\sim \mathrm{Normal}\left( \frac{Central}{V_c}, σ_{pk} \right) \\ yPD &\sim \mathrm{Normal}\left( R, σ_{pd} \right) \end{align*}\]