# Load a pre-trained text embedding model from HuggingFace
loaded_model = hgf"avsolatorio/NoInstruct-small-Embedding-v0"
const encoder = loaded_model[1]
const llm = loaded_model[2];
# Define how to get a patient's embedding
get_embedding(subj::DeepPumas.Pumas.Subject) = get_embedding(subj.covariates(0).Description)
function get_embedding(context)
enc = encode(encoder, context)
out = llm(enc)
return out.pooled
end
# Get the embeddings for all patients and put it in a matrix
X_train = mapreduce(get_embedding, hcat, train_pop)
X_test = mapreduce(get_embedding, hcat, test_pop)DeepNLME with Complex Covariates
Embeddings, Text Data, and Advanced Applications
Niklas Korsbo
2025-10-12
Complex Covariates in NLME
The Data Challenge
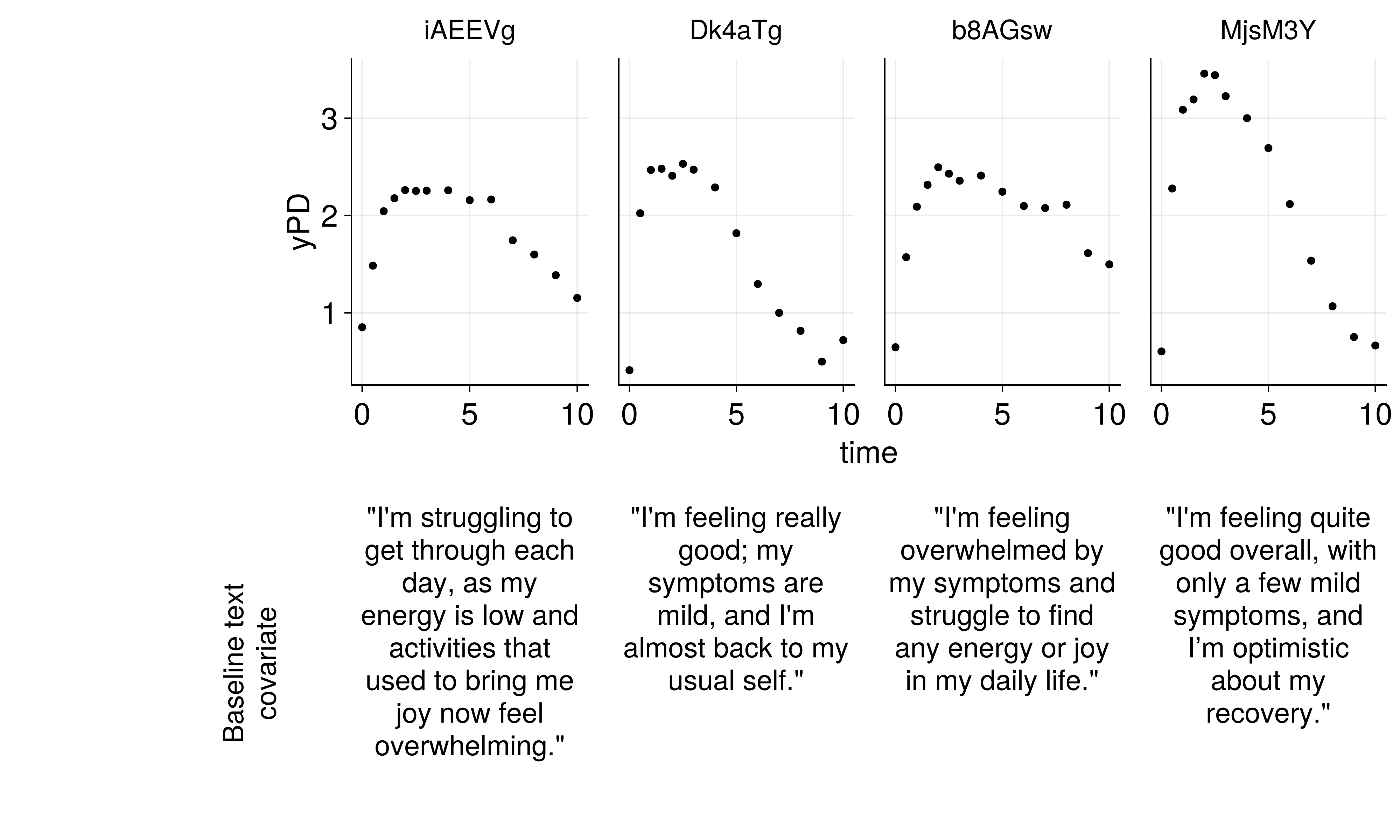
Challenge: How do we use rich text descriptions as covariates in NLME models?
Traditional NLME with Simple Covariates
Good predictions, but missing information from complex covariates
Patient Embeddings
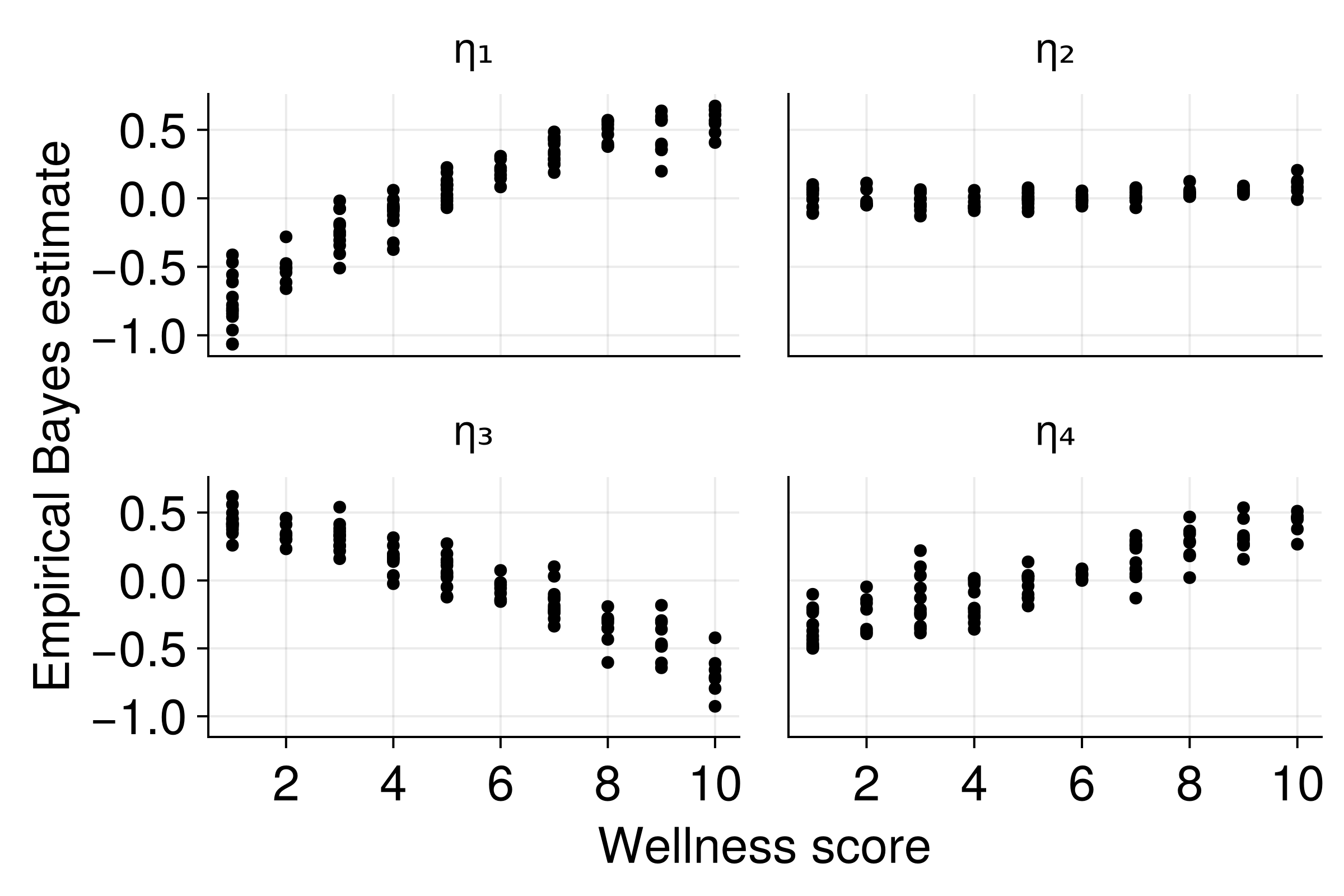
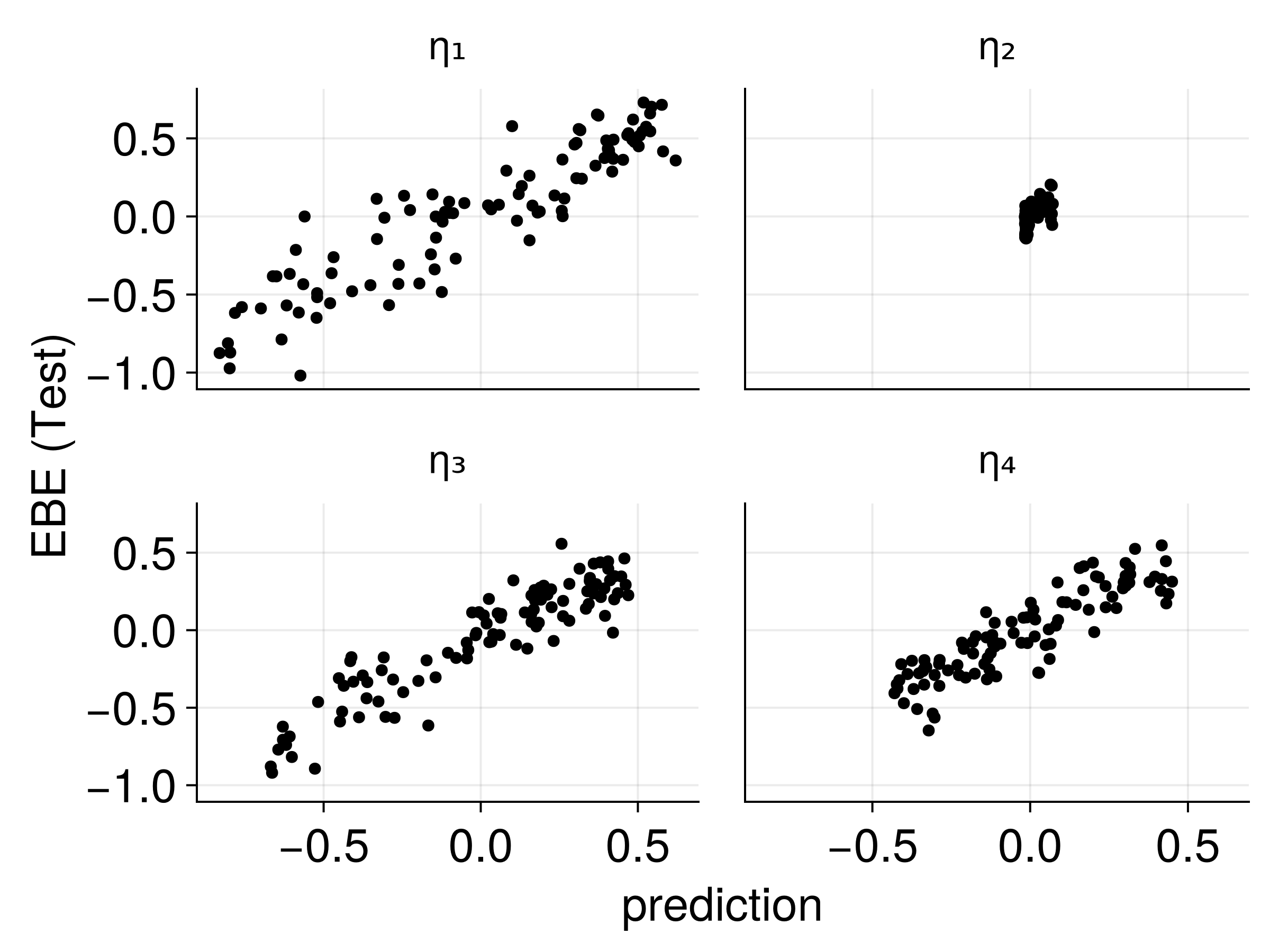
EBEs as Patient Embeddings
Key insight: EBEs encode patient-specific information as low-dimensional vectors!
Validation: Known Relationships
EBEs capture the underlying patient characteristics!
Text Embeddings
The Ease of Creating Embeddings
Embedding Subspacing
- Consider the embedding space as a “meaning space”
- The original model had Shakespeare and Twitter in its training
- Our data are all about describing wellness
- Our data should be on a low-dimensional manifold of the embedding space
Spatial patterns (T-SNE)
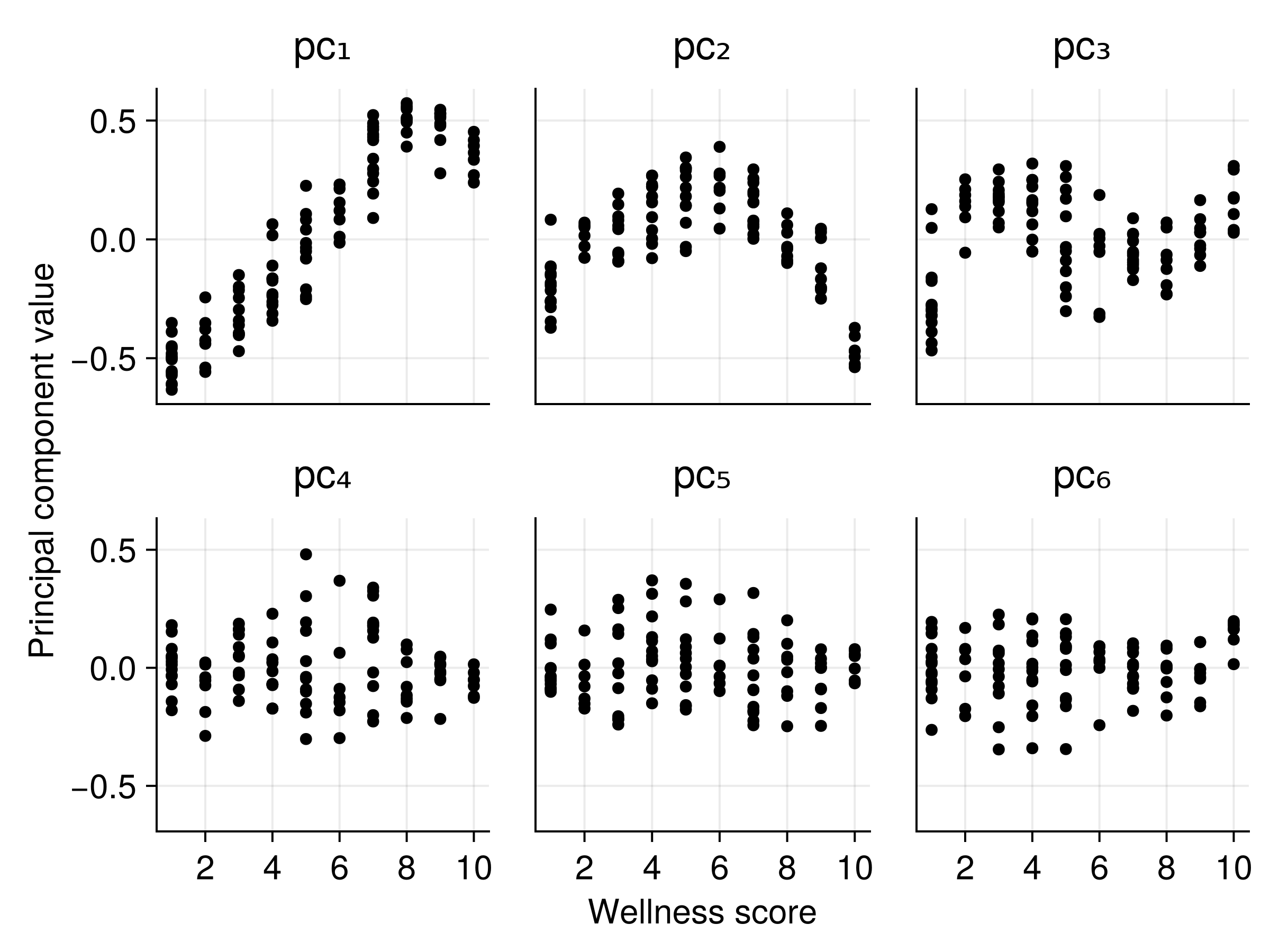
Principal components of the embeddings
Text embeddings capture meaningful clinical information!
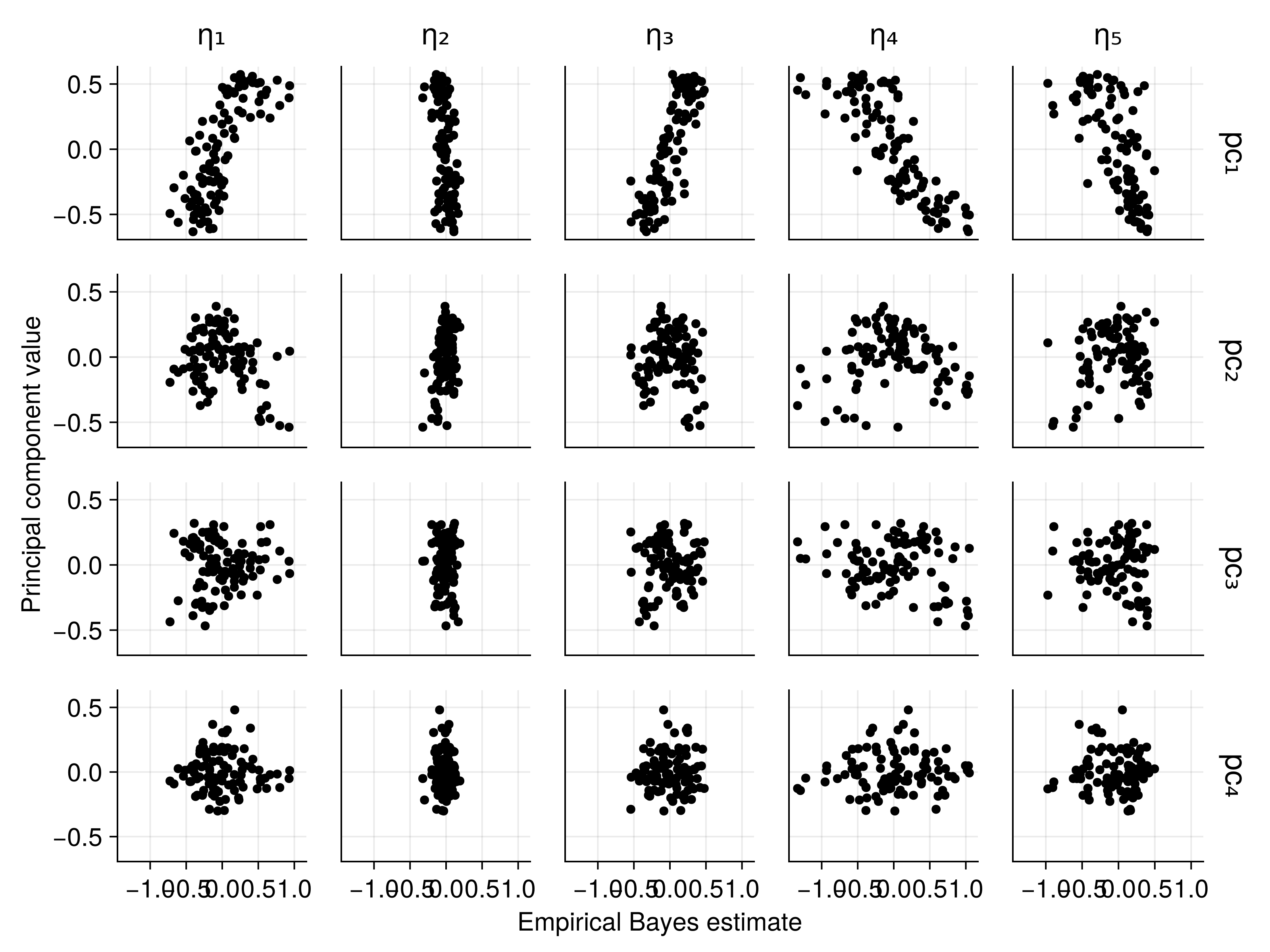
Connecting Embeddings to EBEs
Strong correlations between text embeddings and patient-specific parameters!
Predicting Patient Parameters
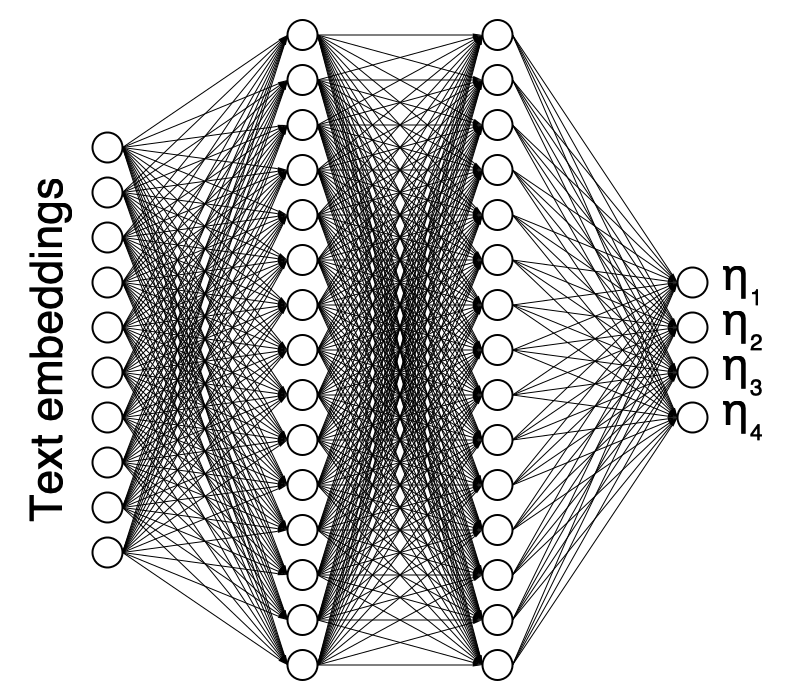
Neural Network Architecture
Text → Embeddings → Neural Network → Patient Parameters
Augmented NLME Models
Usage with NLME
Multiple approaches available:
- Use embeddings as NLME covariates
- Potential dimension reduction first
- Whatever covariate technique you want
- Use embeddings as observations
- FREM modelling?
- Fully joint modelling (requires new algorithms to be feasible)
- Augment existing models
- Predict posterior from embeddings
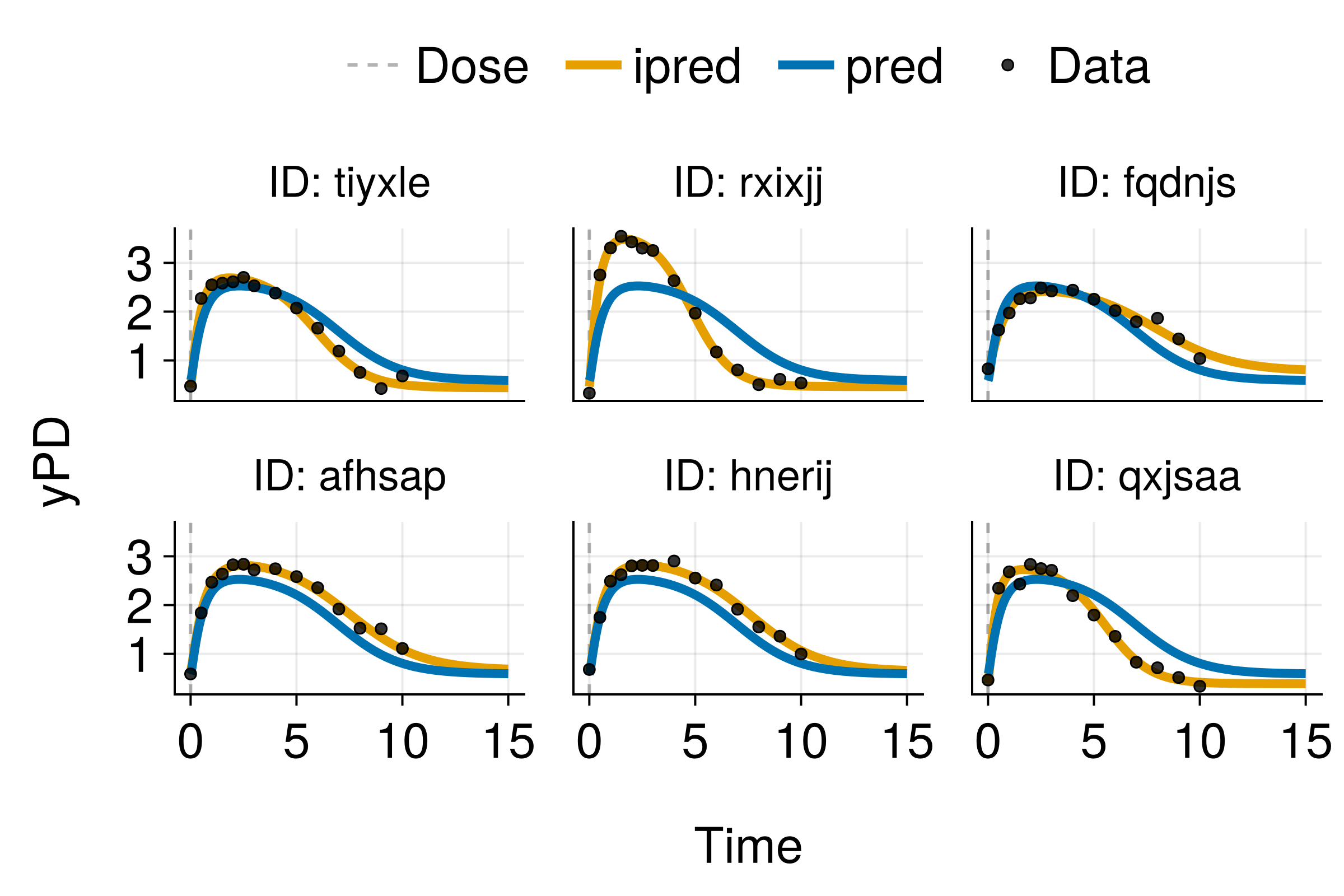
Embedding-Augmented Predictions
Significant improvement using text embeddings!
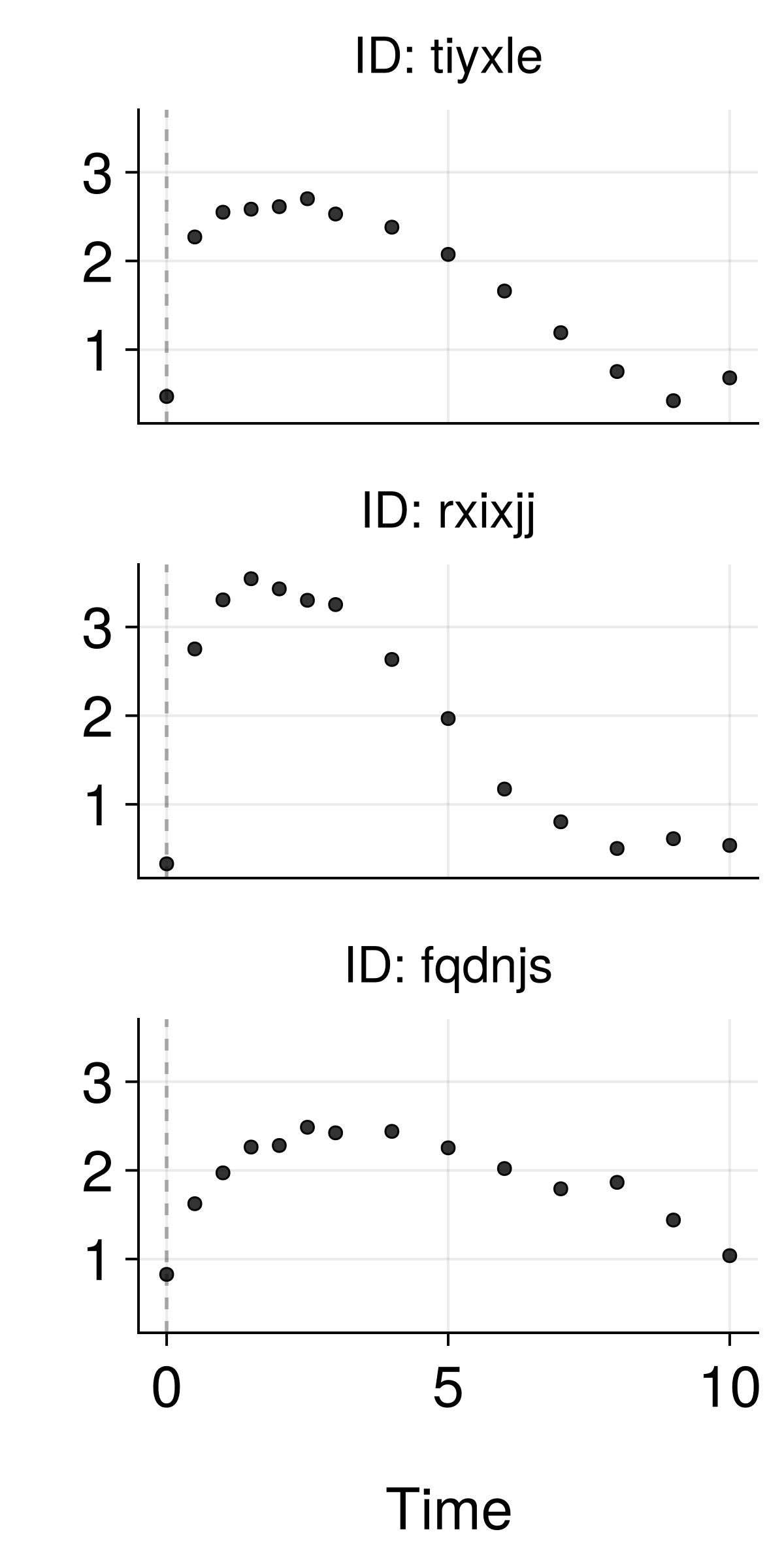
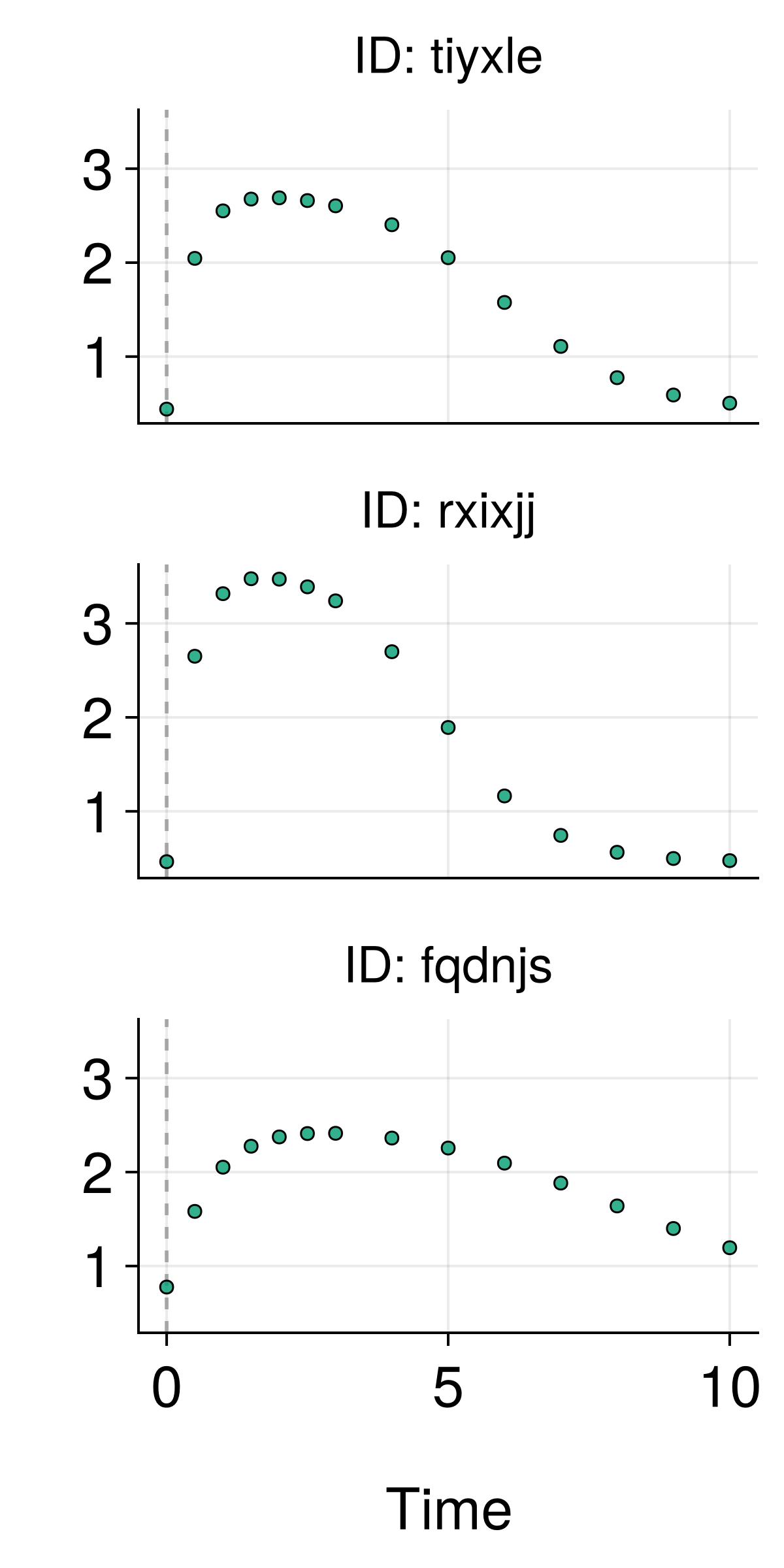
Improved Population Modeling
Before (traditional NLME) 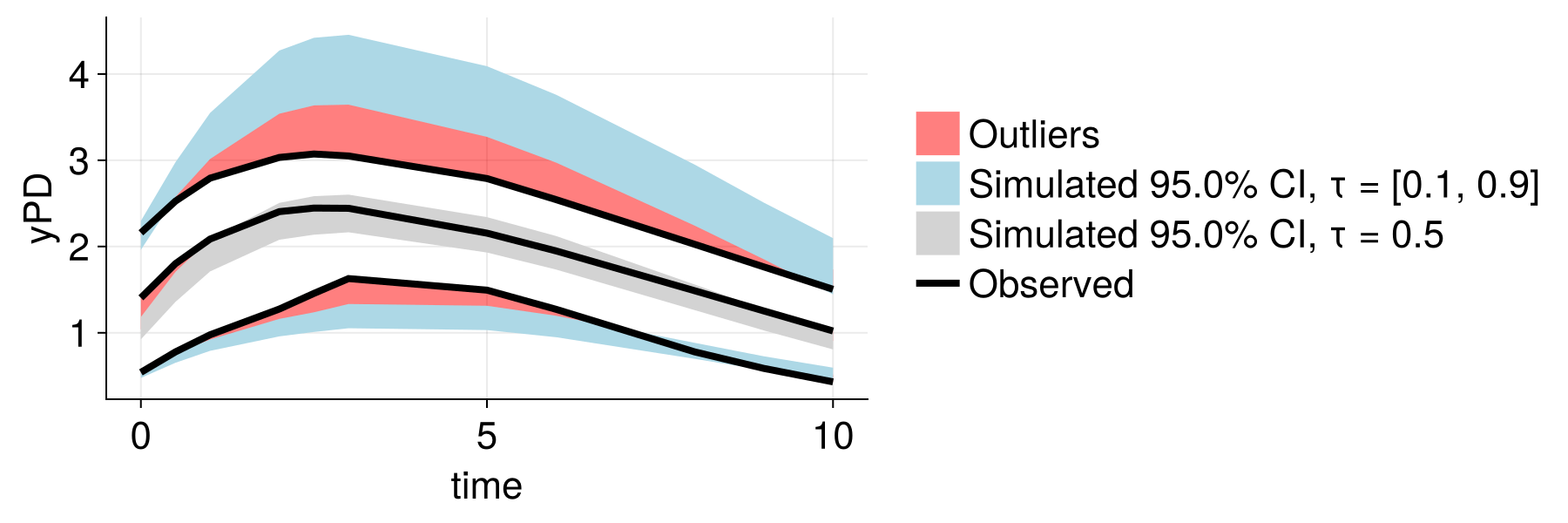
After (embedding-augmented) 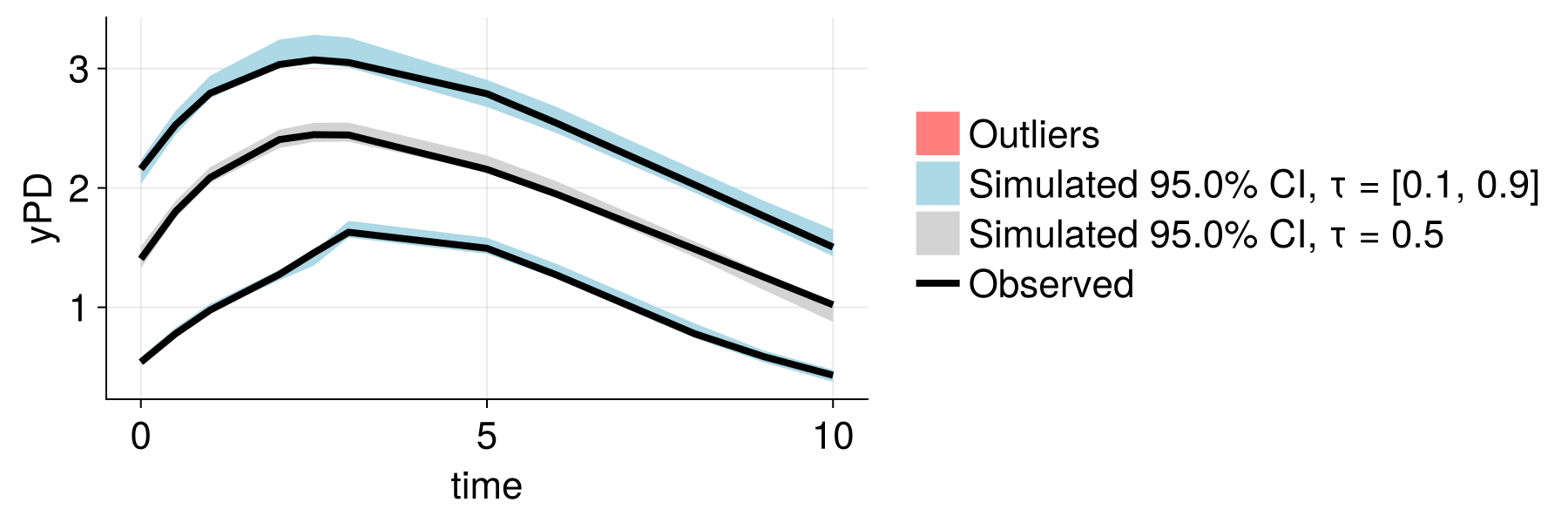
Better population-level predictions and reduced unexplained variability!
Generalization to Other Data Types
Embeddings from Any Data
- Text (clinical notes, patient descriptions)
- 2D Images (X-rays, histology, photos)
- 3D Images (CT scans, MRI - limited model availability)
- Omics data (genomics, proteomics - specialized models)
- Time series (ECG, continuous monitoring)
- Mixed modalities (combining multiple data types)